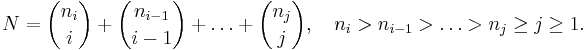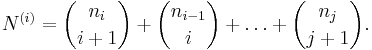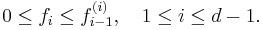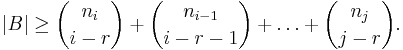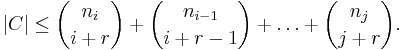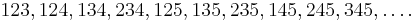Kruskal–Katona theorem
In algebraic combinatorics, the Kruskal–Katona theorem gives a complete characterization of the f-vectors of abstract simplicial complexes. It includes as a special case the Erdős–Ko–Rado theorem and can be restated in terms of uniform hypergraphs. The theorem is named after Joseph Kruskal and Gyula O. H. Katona. It was independently proved by Marcel Schützenberger, but his contribution escaped notice for several years.
Contents |
Statement
Given two positive integers N and i, there is a unique way to expand N as a sum of binomial coefficients as follows:
This expansion can be constructed by applying the greedy algorithm: set ni to be the maximal n such that 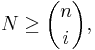 replace N with the difference, i with i − 1, and repeat until the difference becomes zero. Define
replace N with the difference, i with i − 1, and repeat until the difference becomes zero. Define
Statement for simplicial complexes
An integral vector (f0, f1, … fd −1 ) is the f-vector of some (d −1 )-dimensional simplicial complex if and only if
Statement for uniform hypergraphs
Let A be a set consisting of N distinct i-element subsets of a fixed set U ("the universe") and B be the set of all (i −r )-element subsets of the sets in A. Expand N as above. Then the cardinality of B is bounded below as follows:
Suppose that U is the union of the sets in A and that C is the set of all (i + r)-element supersets of the sets in A. Then the cardinality of C is bounded above as follows:
Ingredients of the proof
For every positive i, list all i-element subsets a1 < a2 < … ai of the set N of natural numbers in the reverse lexicographic order. For example, for i = 3, the list begins
Given a vector f = (f0, f1, …, fd −1 ) with positive integer components, let Δf be the subset of the power set 2N consisting of the empty set together with the first fi − 1 i-element subsets of N in the list for i = 1, …, d. Then the following conditions are equivalent:
- Vector f is the f-vector of a simplicial complex Δ.
- Δf is a simplicial complex.
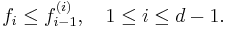
The difficult implication is 1 ⇒ 2.
References
- Kruskal, J. B. (1963), "The number of simplices in a complex", in Bellman, R., Mathematical Optimization Techniques, University of California Press.
- Katona, G. O. H. (1968), "A theorem of finite sets", in Erdős, P.; Katona, G. O. H., Theory of Graphs, Akadémiai Kiadó and Academic Press.
- Knuth, D., The Art of Computer Programming, pre-fascicle 3a: Generating all combinations. Contains a proof via a more general theorem in discrete geometry.
- Stanley, Richard (1996), Combinatorics and commutative algebra, Progress in Mathematics, 41 (2nd ed.), Boston, MA: Birkhäuser Boston, Inc., ISBN 0-8176-3836-9.
External links
- Kruskal-Katona theorem on the polymath1 wiki